알고리즘/알고리즘 문제풀이
dijkstra_Leetcode_787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops [swift]
Downey
2025. 2. 24. 17:45
https://leetcode.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/description/
요구사항
- 이동가능한 간선을 주고, 시작점과 도착점을 준다. 이 때, k번 이하로 이동하는 경로를 사용해야한다.
- 가능한 경로가 없을 때, -1을 반환한다.
- 가장 작은 cost를 반환한다.
문제접근
- 매개변수 flights로 graph 생성, djikstra 시작 준비.
- 정답을 저장할 costs, queue를 선언하고 매개변수 src를 기준하여 초기값 주입
- djikstra 시작.
- queue의 첫번째 element 추출
- graph를 참조하여, nextFlight를 순회한다.
- if costs[nextDst].isEmpty 라면, 새로운 정보를 costs[nextDst]와 queue에 추가한다.
- else 일 때 costs[nextDst]에서, nextTransfer와 동일한 값을 가진 index 찾는다.
- 있다면, 해당 index의 정보를 cost로 비교하여 더 효율적인 값으로 대체한다.
- 없다면, 새로운 환승 정보를 가진 다른 경우이므로, 새로운 element를 추가한다.
와중에 발생한 디버깅
- 처음에는 with at most를 잘 못 해석하여, 정확한 k를 요구한다고 생각했다. 근데 k 이하의 환승이 요구사항이었다.
- 디버그 중 circling이 일어나는 것을 눈치챘다. ( time out이 발생해서 IDE에서 빌드해서 알게 됨 )
- 첫 번째 testCase를 확인 할 경우, 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0 으로 circling하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
- 떄문에, 겹치는 환승 횟수가 없을 때, 새로운 환승 횟수와 요금이 더 비효율이라면 해당 경우를 무시한다. 이를 통하여 circling을 제거한다.
- transfer는 반복마다 올라간다. 그런데, 해당 문제에서 0->1->2로 이동시 환승을 1회로 간주한다.
- 때문에 fliter처리 시, transfer - 1을 수행했다.
아쉬운 나의 정답 코드
더보기
class Solution {
struct FlightInformation {
var cost: Int
var transfer: Int
}
func findCheapestPrice(_ n: Int, _ flights: [[Int]], _ src: Int, _ dst: Int, _ k: Int) -> Int {
var costs = [[FlightInformation]](repeating: [], count: n) // 목적지에 도착하는 여러가지 경우의 수를 고려한다.
var graph = [Int: [(Int, Int)]]() // [src, [(dst, cost)]]
var queue = [(Int, FlightInformation)]() // current
for flight in flights {
if graph[flight[0]] == nil {
graph[flight[0]] = []
}
graph[flight[0]]?.append((flight[1], flight[2]))
}
// 시작점을 초기화
let srcStart = FlightInformation(cost: 0, transfer: 0)
costs[src] = [srcStart]
queue.append((src, srcStart))
// 우선순위 queue에 시작점 추가, 어라 우선순위 queue여야하는가? 가능한 모든 이동 가능한 경로를 고려해야 하므로 아닌것 같은데?
// dijkstra 시작. ->
while !queue.isEmpty {
let current = queue.removeFirst()
let (currentStr, currentFlight) = current
let nextTransfer = currentFlight.transfer + 1
for nextFlight in graph[currentStr, default: []] { // graph: [src, [(dst, cost)]] nextFligt: (dst, cost)
let nextDst = nextFlight.0
// if nextDst == src { continue } // nextDst가 초기 위치로 돌아가는 경우가 있다. 이 코드를 주석처리하면 전체 성능이 더 나빠짐.
let price = nextFlight.1
if costs[nextDst].isEmpty {
let nextValue = FlightInformation(cost: price + currentFlight.cost, transfer: nextTransfer)
costs[nextDst].append(nextValue)
queue.append((nextDst, nextValue))
queue.sort(by: {
$0.1.cost < $1.1.cost
})
} else {
if var targetIndex = costs[nextDst].firstIndex(where: {
$0.transfer == nextTransfer
}) {
if costs[nextDst][targetIndex].cost <= currentFlight.cost + price { continue }
let nextCost = costs[nextDst][targetIndex].cost < currentFlight.cost + price
? costs[nextDst][targetIndex].cost
: currentFlight.cost + price
let nextValue = FlightInformation(cost: nextCost, transfer: nextTransfer)
costs[nextDst][targetIndex] = nextValue
queue.append((nextDst, nextValue))
queue.sort(by: {
$0.1.cost < $1.1.cost
})
} else {
let maxValue = costs[nextDst].max(by: {$0.cost < $1.cost})!
// 초기위치가 아니라 도중으로 돌아가서 circling하는 경우도 있는 것 같다.
if price + currentFlight.cost >= maxValue.cost // circling에 대한 예외처리.
&& nextTransfer >= maxValue.transfer {
continue
}
let nextValue = FlightInformation(cost: price + currentFlight.cost, transfer: nextTransfer)
costs[nextDst].append(nextValue)
queue.append((nextDst, nextValue))
queue.sort(by: {
$0.1.cost < $1.1.cost
})
}
}
}
}
let dstCosts = costs[dst]
let filtered = dstCosts.filter { $0.transfer - 1 <= k }
// costs에서 목적지 index의 정보를 추출. filter로 적합k(k 이하 경유)값을 가진 element 추출. isEmpty? -1 : min()
return filtered.isEmpty ? -1 : filtered.min(by: { $0.cost < $1.cost })!.cost
}
}해당 코드는 효율성에서 나쁜 결과를 얻었다.
그래서 더 좋은 코드를 찾는다...
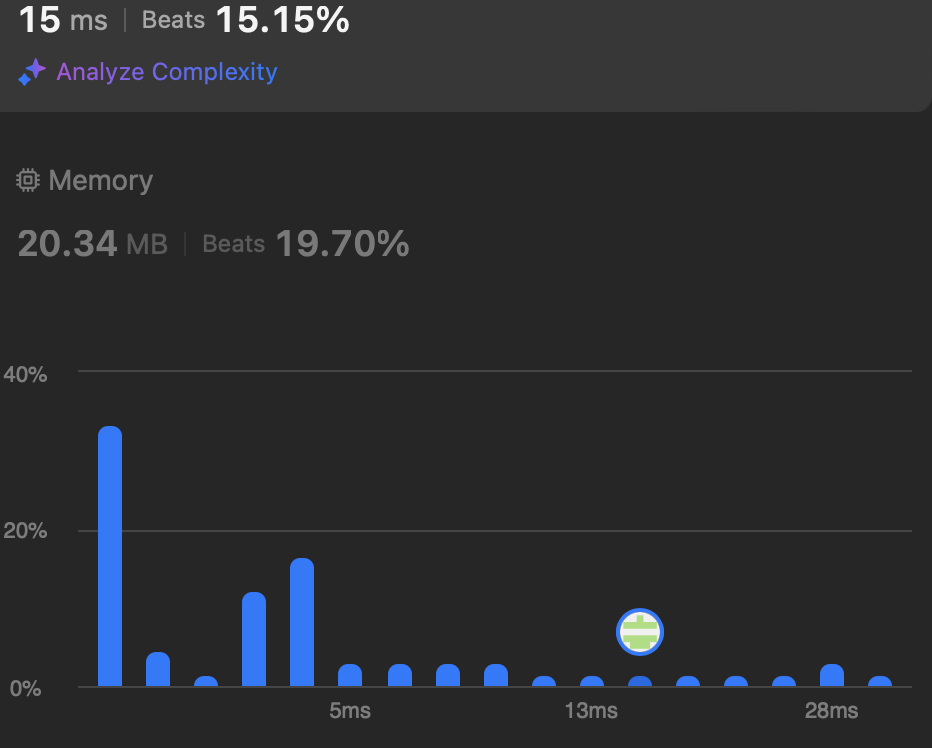
정답코드
화가난다... 단순반복문에 가까운 코드...
“K Stops 제한”이 있는 경우, 단순 BFS가 더 적합
• 다익스트라는 한 번 방문한 노드의 거리를 갱신하면 더 이상 방문하지 않음
• 하지만 이 문제에서는 같은 노드를 방문하더라도 K개 이하의 경유 조건을 만족해야 하므로, 여러 번 방문이 필요할 수 있음
• 따라서 “비용이 최소인 경로”보다 “경유 횟수(K)를 제한하는 BFS”가 더 적합
💡 즉, 다익스트라는 출발 → 목적지까지 가는 최단 경로를 보장하지만,
이 문제는 “경유 횟수 제한이 있으므로 비용이 적은 경로라도 탐색을 중단하면 안 된다.”
라고 GPT가 답변했다...
아래 코드는 k번 반복을 수행함으로써, 내 코드에서 관리했던 transfer정보가 불필요하다.
더보기
class Solution {
func findCheapestPrice(_ n: Int, _ flights: [[Int]], _ src: Int, _ dst: Int, _ k: Int) -> Int {
var prices = Array(repeating: Int.max, count: n)
prices[src] = 0
for i in 0..<k+1{
var temp = prices
for flight in flights{
let start = flight[0]
let end = flight[1]
let p = flight[2]
if prices[start] != Int.max{
temp[end] = min(temp[end], p + prices[start])
}
}
prices = temp
}
let value = prices[dst]
return value != Int.max ? value : -1
}
}